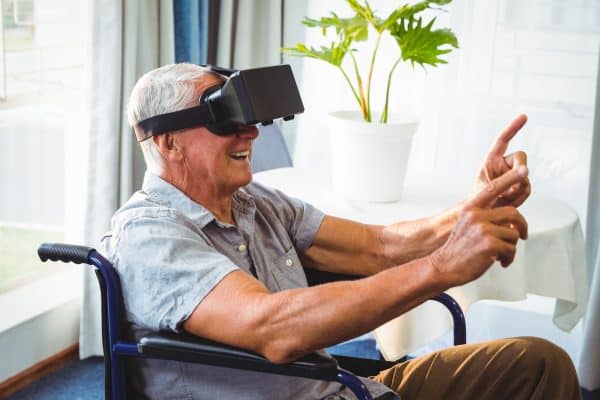
Americans 50+ are the fastest-growing group of marijuana users. According to AARP, people are using medical marijuana at midlife to treat a host of age-related issues. They’re seeking relief from conditions like arthritis, chronic pain, sleeplessness and so on.
Thousands of websites offer information on cannabis, but it’s hard to tell which are impartial and which are sponsored by specific marijuana producers or sellers. This post simplifies confusing data you’ll find on the internet. You’ll learn what you need to know to become an informed consumer of medical marijuana at midlife.

From ancient drug to big business
People have used cannabis since ancient times to treat pain and other ailments. But marijuana was illegal in the US for many years. Now 33 states have legalized medical marijuana. Eleven states and the District of Columbia have authorized its recreational use as well.
The Marijuana Business Factbook estimates the size of the US marijuana market to be as high as $13.7 billion in 2019, $5.2 billion of which is for medical marijuana. It forecasts that by 2023, retail sales of cannabis will hit a possible $30.4 billion ($8.4 billion for medical marijuana).
Cannabis sales have already generated millions in tax revenue for the states where recreational or medical marijuana is legal. Similarly, the nascent industry is creating thousands of jobs and investment opportunities galore.
 You will find more infographics at Statista
You will find more infographics at Statista
Medical marijuana benefits
The only FDA-approved use of cannabis is for the treatment of two rare but severe forms of epilepsy. There are studies that suggest medical marijuana may benefit several other conditions, but evidence remains inconclusive.
The Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) still classifies marijuana as a Schedule I substance, in the same category as heroin, LSD, Ecstasy and peyote. Schedule I drugs, according to the DEA, “have no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse.”
There are strict regulatory barriers to double-blind, randomized clinical trials of cannabis. Thus government regulations currently prohibit the type of testing that would be needed to assess the safety and benefit of medical marijuana.
Existing evidence varies
Considerable gives the following list of conditions that medical marijuana may improve:
- Conclusive or substantive evidence
- chronic pain
- nausea and vomiting due to chemotherapy
- spasticity due to multiple sclerosis
- Moderate evidence
- sleep disorders
- fibromyalgia
- unwanted weight loss
- Turette syndrome
- anxiety
- PTSD
- Promising results but no real evidence
- tremors due to Parkinson’s Disease
- digestive issues such as irritable bowel syndrome
In summary, medical marijuana can potentially alleviate the symptoms of many different physical and mental health problems. But there’s scant proof. At best it exists alongside other alternative therapies that show promise but are not yet embraced by the medical establishment.
Hemp, marijuana, cannabis, weed: what’s the difference?
Cannabis is an all-encompassing term that indicates the plant genus Cannabis. Cannabis plants may be further differentiated by species as Cannabis sativa, Cannabis indica, or a hybrid. These distinctions are often confusing. Popular wisdom links indica with relaxation and sativa with energy, but experts question whether there should really be a distinction between the two.
Cannabis plants contain over 80 different cannabinoids and over 125 terpenes. Let’s focus on cannabinoids. Cannabinoids are 21-carbon molecules that block or stimulate endocannabinoid receptors in your body.
Your body also produces its own cannabinoids. The appeal of cannabis as a medical treatment, however, is how it binds to cannabinoid receptors in the body to inhibit pain, nausea, etc.
CBD and THC
CBD, or cannabidiol, is a cannabinoid that has received tons of attention in recent years. The other well-known cannabinoid in this type of plant is THC (tetrahydrocannabinol).
The “high” that people get from cannabis is largely due to its concentration of THC. People take CBD, in contrast, to get cannabis’ wellness benefits without its psychoactive effects.
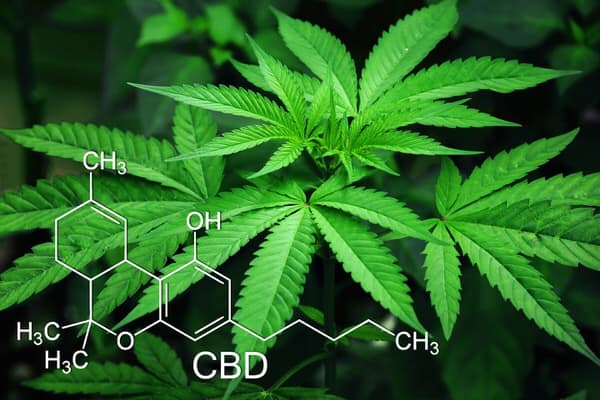
Hemp
Hemp plants are those that contain less than 0.3% THC. Uses and types of hemp plants vary.
Hemp is one of our earliest domesticated plants. It requires little to no pesticides, controls soil erosion, and has many industrial applications. For example, hemp is used for textiles, paper, biodegradable plastics, fuel, and health food.
Industrial grade hemp and medicinal hemp are different. For instance, growers may breed industrial hemp for the strength of its fibers. Medicinal hemp growers, on the other hand, usually aim to maximize the plant’s level of CDB.
Marijuana
In contrast to cannabis plants grown for industrial purposes or to maximize CBD, marijuana denotes the plants grown to yield the greatest levels of THC. They often contain 5%-20% or even greater concentrations of THC.
Marijuana cultivation continues to be illegal in much of the US. Even where voters have approved recreational marijuana, agricultural regulations and testing processes still vary.
CBD: the latest miracle drug?
Medgadget estimates the US market for CBD oil to be growing at a compound annual growth rate of 36% per year. They project the CBD market will increase from $462 million in 2018 to $2.2 billion in 2023.
Significantly, the 2018 Farm Bill lifted a ban on the cultivation of hemp, the cannabis plant variety that contains less than 0.3% THC on average.
Now you can buy CBD oils, tinctures, capsules, creams, bath salts and more at your local mall. Or on Amazon. But with many of these products, you don’t really know what you’re getting.
Hemp seed oil vs. CBD oil
Although both hemp seed oil and CBD oil are popular in the beauty and wellness space, they aren’t the same. Hemp seed oil (also called cannabis seed oil) comes from the seeds only.
CBD oil (which may be labeled hemp oil or full-spectrum hemp oil) contains more CBD and other terpenes extracted from the whole hemp plant. From there, it gets even more complicated.

Not all CBD oil is the same, either
Medicinal hemp varies in quality and potency (concentration of CBD). According to the Ministry of Hemp, there are 5 things to consider when deciding which CBD products to buy.
1. Extraction methods
CBD has to be extracted from the hemp plant. Most super-cheap CBD oils come from companies that use toxic chemicals like butane or propane to extract the CDB.
Pharmaceutical-grade organic ethanol is a better and safer extraction method, and it tends to yield the highest level of cannabinoids.
Another way to extract CBD oil is “supercritical CO2 extraction.” This method requires expensive equipment and more complex refinement process. However, some think it yields the purest type of CBD oil.
2. Where and how the hemp is grown
Hemp is a hyperaccumulator plant, meaning that it absorbs anything that is present in the ground or that was farmed there previously. So not only do you want to buy CBD oil that comes from quality plants. You want to make sure your hemp wasn’t grown in dirt with a high concentration of metals or other bad chemicals.
Choosing CBD oil from organically-grown hemp may help you avoid toxins like metals in the soil.
3. Amount of THC present
All hemp plants must contain no more than 0.3% THC. And yet, depending on the extraction and manufacturing process, the resulting oil may contain a more concentrated form of THC than the plant does. Check the label and ask for test results to make sure your batch has less than 0.3% THC.
4. “Whole plant” or “full-spectrum” CBD
Similar to the need to make sure you’re buying CBD oil and not hemp seed oil, you want to avoid oils made from “CBD isolates” in favor of those made from the whole plant. Isolates are cheaper but lack beneficial elements gained from using the entire plant.
Full-spectrum CBD oil includes terpenes, flavonoids, and other cannabinoids that work alongside the CBD to benefit your health.
5. Third-party lab results
High-quality CDB oils will provide results of tests made by third parties. They may put lab results on their website. Some include specific results in their packaging. If you don’t see published lab results, feel free to ask.

The entourage effect
CBD oil appeals to people who want the medicinal benefits of cannabis without its psychoactive effects. At the same time, products that combine CBD and THC may be more effective at addressing symptoms.
The entourage effect refers to the concept that the whole is better than just a part. To be most beneficial, medical marijuana at midlife (or any age) should combine rather than isolate different cannabinoids and other elements of the cannabis plant.
Summary
Selecting medical marijuana at midlife is complicated. Finding the right product to help your chronic back pain, for example, might be much harder than finding some weed to smoke this weekend. You have to study a lot of websites, read labels and talk with people in the know.
This primer should help you navigate the basics. You now know how to assess CBD quality, why you might consider a blend of CBD and THC, and what questions to ask based on your personal situation.
Reply in the comments with your own tips and experience. I look forward to hearing about your search for medical marijuana at midlife.
Images via: Shutterstock, Pexels, Statista



